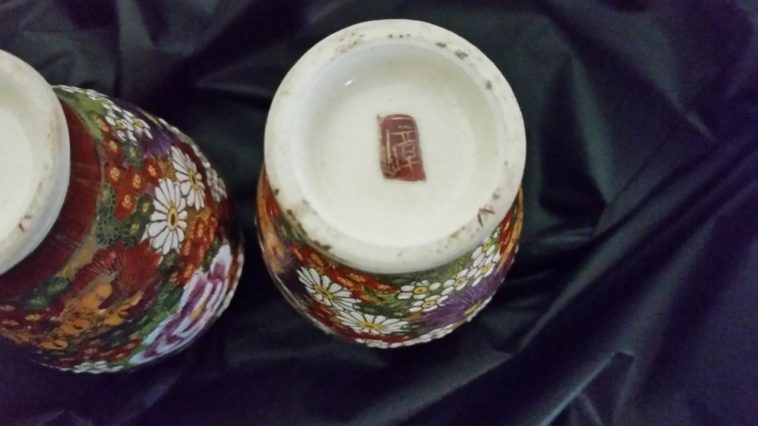
Kutani is the Japanese word for Nine Valleys. It is the name of a village, an area where the two characters ‘Ku’ is nine, and ‘tani’ is valley. Kutani is an ancient place where pottery was made in 1655. Since this is the place where Kutani art originated, every piece is marked with the Kutani symbol.
Just so, How do you identify Kutani ware?
Marking is getting more simple, However we almost always get also at the minimum the Kutani mark – 九谷 –. This mark is often combined with – 日本 – Nihon (Japan). Ceramics are also always identified with a Kutani mark – 九谷 – . The mark is also often combined with – 日本 – Nihon (Japan).
What is the difference between Kutani and Satsuma? Earthenware pottery – All Satsuma is earthenware. You can tell it from porcelain by the weight. … If the decoration looks like Satsuma but it is porcelain, then it is likely Kutani. (Kutani uses a lot of red and gold, this can be also be a giveaway.)
Similarly, What is Kutani China worth?
Generally, collectors consider Kutani pieces such as Johanna’s example to be more desirable and valuable than the more commonly found Geisha Girl. Whereas a Geisha teapot in this size might bring $25, the Kutani teapot would more likely be valued in the $50 to $75 range in a shop.
What is Japanese Moriage?
Moriage is a common name on slip or colored clay string decoration, mostly on Japanese porcelain, in look not unlike ‘cake frosting’ in which a diluted clay has been used to give the piece a three dimensional appearance.
Are Japanese tea sets worth anything?
For instance, one seller has an occupied Japan teacup and saucer listed for a little over $10; yet, more extensive sets, like this 10 piece teacup set, as well as those made prior to the 20th century can be worth a few hundred dollars.
What is Meiji Satsuma?
The Satsuma with which most people are familiar is late Satsuma or nishikide. It is a distinctive Japanese pottery present during the Meiji period (1868 to 1912). The ceramic example has a warm cream, ivory to beige background with a crackled glaze. … A Goodwill store “Satsuma” purchase.
What is Moriage Satsuma?
Moriage is a slip decoration of raised enamels. It occurs on Satsuma wares as early as circa 1890 but tends to be more carefully applied on early pieces. Moriage also seems to be limited to pieces made outside of the Satsuma domain while being typical for Kyoto Satsuma ware.
How do I know if I have a Satsuma vase?
The ceramics are fired at lower temperatures than porcelain, so Satsuma is a kind of hybrid porcelain-pottery. Collectible Satsuma, dating from the mid-19th century on, may be identified by its ornately decorated polychrome and gold designs on an ivory crackle-glazed ground.
Is Kutani China still made?
There are now several hundred companies which produce Kutani ware. Many artists today are located in Komatsu, Ishikawa and Terai.
How old is Kutani?
It is believed that Kutani ware was first manufactured in what was the Kaga Province of Japan in the seventeenth century, supposedly inspired by the techniques used at Arita. However production of Kutani ware ceased towards the end of the 17th century, and it was not until the 19th century that production was revived.
What is Japanese Kutani porcelain?
Kutani ware, Japanese porcelain made in Kaga province (now in Ishikawa prefecture). The name “Old Kutani” refers to porcelain decorated with heavily applied overglaze enamels and produced in the Kaga mountain village of Kutani. … The bold designs of Kutani ware drew freely from Chinese ceramics, paintings, and textiles.
What does Moriage look like?
Highly stylized flowers, variations of pastel colors, gilding or gold paint, and applied slip decorations are all characteristics of moriage pieces. The moriage style indicates that the piece referenced the late 19th century interest in Japonisme and the worldwide decorative art interest in exotic designs.
What is Satsuma Moriage?
Moriage. Moriage is a slip decoration of raised enamels. It occurs on Satsuma wares as early as circa 1890 but tends to be more carefully applied on early pieces. Moriage also seems to be limited to pieces made outside of the Satsuma domain while being typical for Kyoto Satsuma ware.
What is Japanese Satsuma?
Satsuma ware is a type of earthenware pottery originating from the Satsuma province in southern Kyushu, Japan’s third largest island. … There are two distinct types of Satsuma ware. The original Ko-Satsuma is characterised by a heavy dark glaze, often plain, but occasionally with an inscribed or relief pattern.
What is Moriage?
The term moriage refers to the technique of raised, trailed-slip decoration. It was widely used to decorate all kinds of pottery made in Asia. The best-known moriage may be the ugly, newer Japanese dragonware. These vases could be the product of the Kinkozan family of potters, in production from 1645 until 1927.
Are cups and saucers valuable?
Vintage teacups can be worth quite a lot! You’ll find them priced from $20-$100, even more if it is rare and in mint condition.
What do the numbers on the bottom of tea cups mean?
Look at the numbers on the bottom of the tea set. Numbers represent the code of the manufacturer, a pattern number or its registration number. The number will have “rd” following it if it is the registration number. The number is an important piece in identifying tea set age as you combine all of the previous steps.
What is the most expensive teapot?
Stir crazy: the world’s most expensive teapot
- Officially certified by the Guinness Book of Records, the $3 million Egoist is the most valuable teapot in the world.
- A teapot just for one, the Egoist has been donated to the Chitra Collection of historic and contemporary teapots by owner Nirmal Sethia.
Is Satsuma pottery worth anything?
Because of its long history and popularity through time, the price of Satsuma ware can range from less than one hundred pounds to many thousands of pounds. This makes it a very accessible art form to many collectors including those that are just starting out.
Is Satsuma China valuable?
Satsuma Pottery in the Market Today
The renown of the Satsuma pottery kilns spread far and wide throughout the country. While the Japanese Satsuma vase is one of the most popular objects in the field, any work from this period tends to be quite valuable today.
How do you read Satsuma marks?
Satsuma. Mark: Shimazu family crest above a cartouche, reading: Satsuma Hekizan. The two characters to the right read “Satsuma”. The bottom left is usually written as “zan”, rather than “yama”.